
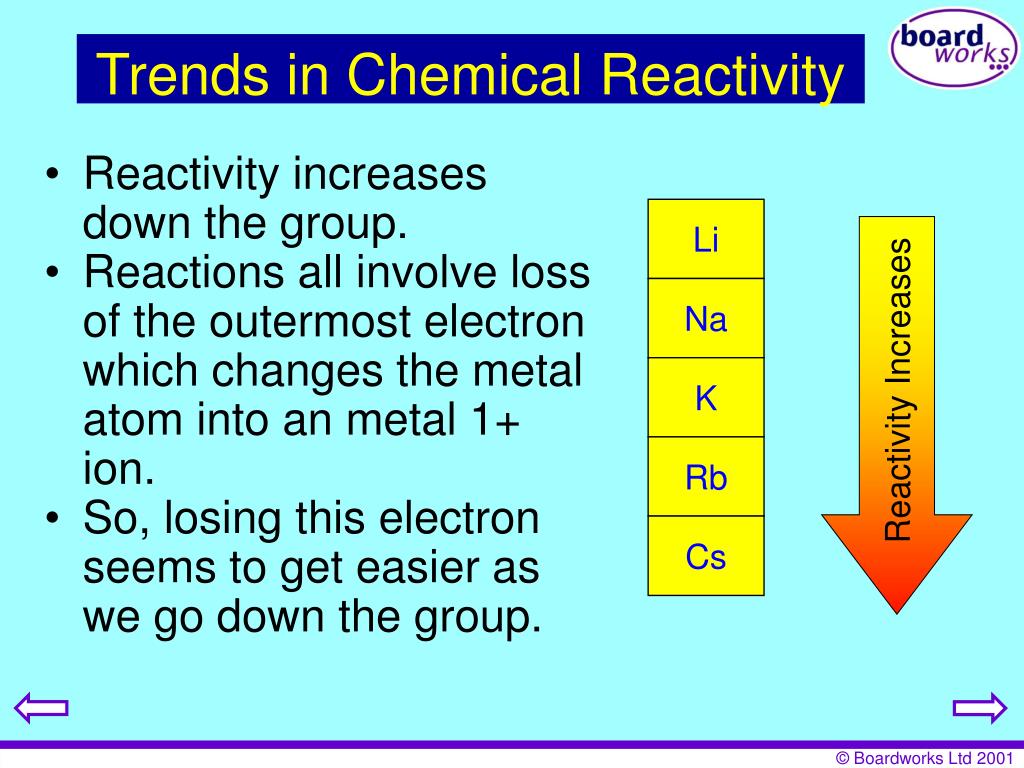
The atomic radius increases as you go down a Group because you are adding energy levels.As you go from left to right, the effective nuclear charge increases because as you are adding protons, you are still in the same energy level so the inner electrons are not increasing.The atomic radius is not how big the atom is but is measured as half the distance between neighbouring nuclei.Properties of elements and their trends Just a note that all the trends are written about in here are in the data booklet provided in the exams but you will still need to know why these trends happen. Relatively stable metals with only moderate reactivity – useful for construction.
#Transition metal reactivity trend full#
The d-block region (This excludes zinc and the elements below it as they have a full d subshell) Reactive metals – but less reactive than group 1. The most reactive group of metals – react strongly with cold water ( Videos). Period: number of occupied (electron) shells Names of special groups with characteristic properties Group Name
(a) Distinguish between the terms group and period in terms of electron arrangement.Ī: (2 Marks) Group: number of outershell/valence electrons The key take away is, that just by looking at where an element is positioned you can immediately know what it's configuration is.Ĭarbon and silicon belong to the same group of the periodic table. The diagram above shows you how the sp,p,d,f blocks are organized.
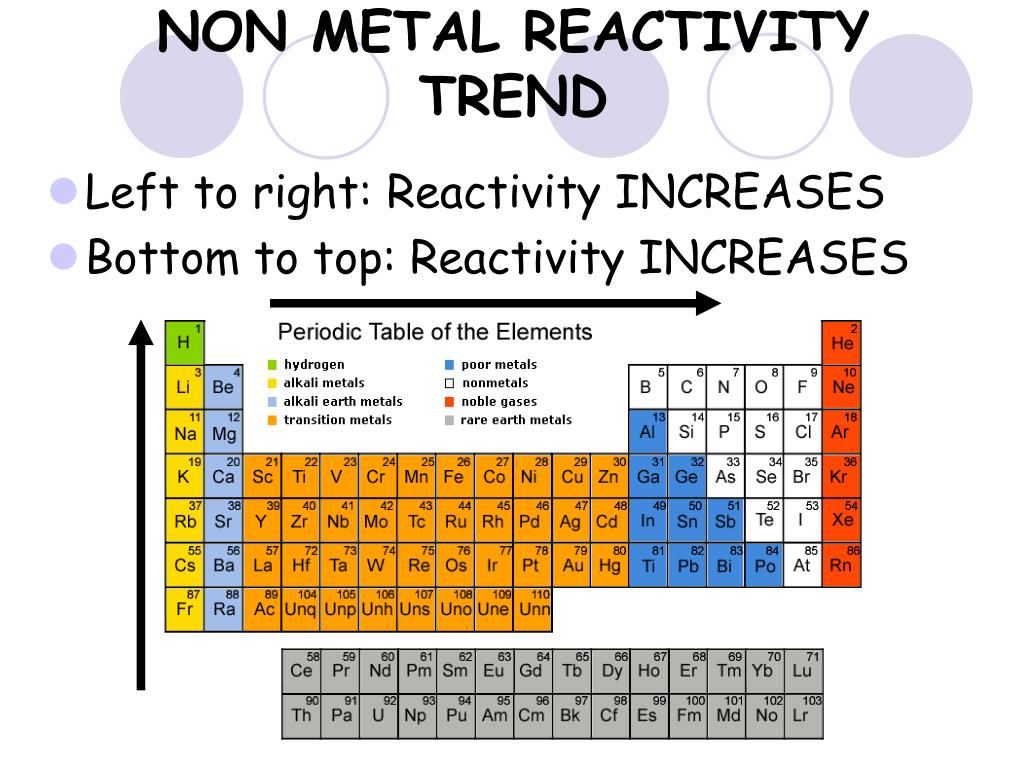
So it's highest sub level in its electron configuration is P and it is filled with three electrons.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
